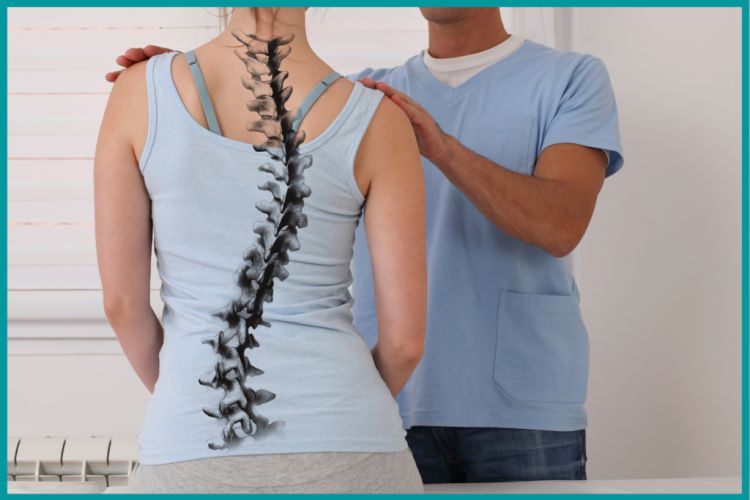
 The causes of scoliosis are unknown. Yes, it is believed that genetic or environmental factors can happen. Scoliosis is defined as the term in which the spine of the person is curved sideways. In some cases, the degree of the curve is stable, while in other cases, it increases over the period.
The causes of scoliosis are unknown. Yes, it is believed that genetic or environmental factors can happen. Scoliosis is defined as the term in which the spine of the person is curved sideways. In some cases, the degree of the curve is stable, while in other cases, it increases over the period.
Scoliosis can be easily diagnosed in childhood or early adolescence by contacting a specialist or a Scoliosis clinic. Scoliosis is defined as spinal curvature in the coronal plane, and the degree of curvature is measured on the coronal plane. A vertical plane from head to foot and parallel to the shoulder, dividing the body into the back and front sections, is called a coronal plane.
Scoliosis treatment depends on the curve’s condition and its causes. In scoliosis,
The curve shaped over three dimensions is usually “S”- or “C”-.
Signs of scoliosis
- Difficulty while walking or running
- Difficulty in breathing
- Difficulty in standing straight
- Uneven shoulder or hips
- Respiratory or cardiac problem
Causes of scoliosis
The causes of scoliosis are classified by etiology at the Scoliosis Clinic.
- Idiopathic: it is the most common and basic type of scoliosis. Idiopathic can be diagnosed by treatment during puberty.
- Congenital: congenital scoliosis can occur in any location of the spine. It is the result of the malformation of one or more vertebrae.
- Neuromuscular: it is the type of scoliosis that generally progresses more rapidly compared to others. Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with cerebral palsy, spinal cord trauma, muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, and spina bifida.
Diagnosis of Scoliosis
Diagnosis of scoliosis can be made by physical examination at a scoliosis clinic, that is, an X-ray, spinal radiography, CT scan, or MRI. The spine curve is considered significant if it is greater than 25 to 30 degrees, and if the curve exceeds 45 to 50 degrees, it is considered severe and requires aggressive treatment.
- X-ray: An X-ray of the spine is usually done to check the causes of pain, such as an infection or fractures.
- CT scan: CT scan is done to check the shape and size of the spine canal, contents, and structure.
- MRI scan: MRI is the procedure of a three-dimensional image of body structure using a powerful magnet and computer technology that shows the spinal cord, nerve roots, and surrounding areas.
Treatment of scoliosis
After confirming the diagnosis of scoliosis, a person can contact a scoliosis clinic so that doctors can check several issues and help them to determine the treatment option. Causes like checking the spinal growth are still changing or increasing, the degree of the spinal curve, the possibility of curve progression, and the location of the curve.
After assessing all the causes, it is time for treatment.
- Observation: At the observation stage, in some cases, the spinal cord is mid enough not to require any treatment. The doctor has to check the progress of the spinal change. In children, it can be done every four or six months, and for adults, it can be done every five years.
- Bracing is helpful if the curve is between 25 to 40 degrees. Bracing is recommended to prevent the curve from progressing. Bracing can successfully stop the progress of the spinal curve. For a better result, bracing has to be checked by the doctor regularly.
- Surgery: surgery is recommended if the spinal curve is greater than 50 degrees. Several factors lead to increased surgical-related risk in older adults with degenerative scoliosis. These factors can be advanced age, being a smoker, being heavyweight, and other health issues.